Causes Periodontal Disease
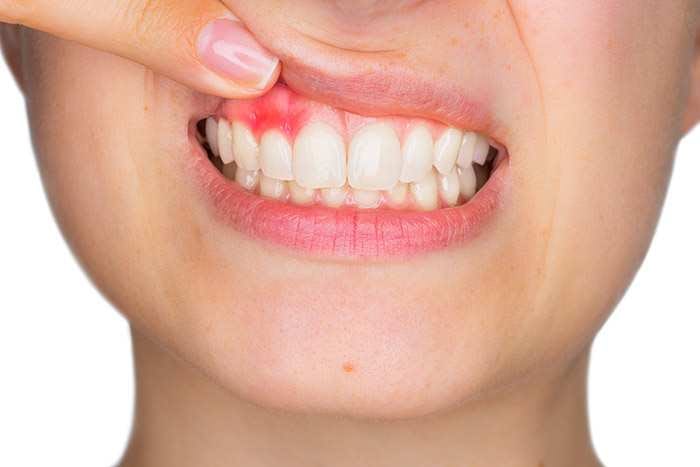
Periodontal disease is also known as Periodontitis is a kind of gum disease characterized by severe inflammation of the gums. It manifests as red, bleeding, or swollen gums. Periodontitis must be treated or it can result in loss of tooth. Special thorough cleaning and, in severe situations, surgery may be required. Periodontitis may be avoided by brushing and flossing regularly. Periodontal disease has many causes. In this article, you will learn more about those causes and how to prevent periodontal disease.
What is Periodontal Disease
Gingivitis can progress to periodontal disease if left untreated. Plaque can spread and build below the gum line over time. Toxins created by plaque bacteria irritate the gums and trigger a persistent inflammatory reaction. In which the body effectively turns on itself, breaking down and destroying the tissues and bone that support the teeth. Gums detach from teeth, causing diseased pockets between teeth and gums. The pockets deepen as the illness develops, and more gum tissue and bone are lost. Teeth might become loose over time and fall out or need to be extracted.
Periodontitis is usually diagnosed using a stage and grade system. The periodontist may give a stage to it that ranges from early to severe and reflects the severity of the illness. Your periodontist may also assign a grade to indicate the rate at which the disease is progressing and the expected response to therapy.
Is Periodontal Disease Reversible?
When periodontal disease is discovered and treated early on, it can be reversed. Gum disease severity changes depending on how far the condition has worsened. Periodontitis, a chronic ailment, is the most advanced stage. The bone structures and soft tissues that support teeth deteriorate as a result of this illness. It can eventually result in tooth loss.
What are the Main Causes of Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is caused by a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. In many situations, the chance of getting periodontitis may be considerably reduced by adopting preventative measures. Those are causes of periodontal disease:
Genetic Predisposition
Even if they follow strict oral hygiene regimens, up to 30% of the population may have a significant hereditary vulnerability to gum disease. Individuals with this genetic propensity are six times more likely to acquire the periodontal disease than those without it. To maintain the oral cavity healthy, genetic testing can be done to detect a vulnerability and early intervention can be conducted.
Poor Dental Hygiene
Dental disease prevention begins at home with basic oral hygiene and a well-balanced diet. Regular dental checkups, which include examinations, cleanings, and x-rays, are also part of the prevention process. The natural dentition and supporting bone structures will be preserved with a mix of excellent home maintenance and expert dental treatment. When bacteria and calculus (tartar) are not eliminated, bacteria toxins harm the gums and bone around the teeth. It causes periodontal disease, which can lead to tooth loss.
Tobacco Use
According to research, one of the most important factors in the development and progression of gum disease is smoking and tobacco use. Smokers are considerably more prone to suffer from calculus (tartar) buildup on teeth, deep pockets in the gingival tissue. In addition to a delayed recovery and healing rate.
Medical Issues
Many medical disorders, such as lung illness, heart disease can exacerbate or hasten the start and progression of gum disease. Diabetes impairs the body’s capacity to use insulin, making it more difficult to regulate and cure bacterial infections in the gums.
Poor Diet and Stress
Because stress reduces the immune system’s ability to combat disease, bacterial infections may be able to bypass the body’s defensive mechanism. In addition to lowering the body’s capacity to fight periodontal diseases, poor diet or malnutrition can have a severe impact on gum health.
Grinding Teeth
The supporting tissue around the teeth can be severely damaged if teeth are clenched or ground. A “poor bite” or misalignment of the teeth is generally related to grinding one’s teeth. Grinding can hasten the advancement of gum disease in people who already have it.
Can You Fix Periodontal Disease?
Periodontists are experts in gum disease therapy and dental implant installation. A periodontist can clean deep pockets effectively using scaling and root planing, as well as administer antibiotics and antifungal drugs to treat infection and slow disease development.
When a tooth or multiple teeth are lost, the periodontist can conduct tissue grafts to stimulate natural tissue regeneration and place dental implants if one or more teeth are missing. The periodontist can recontour the gingival tissue to provide an even and aesthetically attractive appearance if gum recession gives a “toothy” appearance.
Periodontal disease must be avoided if the natural dentition is to be preserved. Preventing the formation, progression, and recurrence of periodontal disease begins with addressing the causes of gum disease and discussing them with your dentist. In Smile Team Turkey, you can also get dental implants, dental crowns, and smile makeover to have a better smile!
Hope this article will help you find out the causes periodontal disease. You can read our previous post on https://dentalguideturkey.com/dental-care-in-babies/